Exploring the Different Materials Used in Ceiling Grids: Steel vs. Aluminum
2024-11-08 16:10:19
When it comes to suspended ceiling systems, the choice of material for the ceiling grid plays a significant role in the overall performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal of the space. Two of the most commonly used materials for ceiling grids are steel and aluminum. Each material has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it important for builders, architects, and interior designers to understand the key differences between steel and aluminum ceiling grids. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of both materials to help you make an informed decision about which ceiling grid material best suits your needs.
1. Steel Ceiling Grids: Durability and Strength
Steel is one of the most commonly used materials for ceiling grids due to its exceptional strength and durability. Steel grids are known for their ability to withstand heavy loads and provide structural stability. Steel is a versatile material that can be used in a wide range of commercial and residential applications.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity: Steel ceiling grids are ideal for spaces that require a higher load-bearing capacity, such as areas with heavy light fixtures, HVAC systems, or ceiling tiles.
Corrosion Resistance: Steel grids are often coated with a protective layer of galvanized steel or powder-coated finish to prevent rust and corrosion. This makes them suitable for both dry and humid environments, providing a long-lasting solution for ceiling systems.
Affordability: Steel ceiling grids are often more affordable than aluminum grids, making them a cost-effective choice for large-scale commercial or residential projects.
While steel is known for its strength and affordability, it is also heavier than aluminum, which can make installation slightly more challenging.
2. Aluminum Ceiling Grids: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Aluminum is another popular material for ceiling grids, known for its lightweight nature and natural resistance to corrosion. Aluminum grids are commonly used in environments where weight and appearance are important considerations.
Lightweight Design: Aluminum ceiling grids are much lighter than steel, making them easier to handle and install. The lightweight nature of aluminum also makes it an excellent choice for ceiling systems where reducing weight is a priority.
Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally resists rust and corrosion without the need for additional coatings, making it suitable for environments with high humidity or moisture levels, such as kitchens, bathrooms, or industrial spaces.
Aesthetic Appeal: Aluminum has a sleek, modern appearance that can complement contemporary interior designs. It can also be anodized or powder-coated to achieve a variety of finishes, enhancing its visual appeal in high-end commercial or residential spaces.
While aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion and easy to install, it is generally more expensive than steel and may not be as strong for supporting heavy loads.
3. Cost Comparison: Steel vs. Aluminum Ceiling Grids
Cost is an important consideration when choosing between steel and aluminum ceiling grids. Both materials come with different price points based on factors such as material costs, manufacturing processes, and coatings.
Steel: Steel ceiling grids are typically more affordable than aluminum grids. The cost of steel is relatively low, and it is readily available in most regions, making it an economical option for large projects or installations that require large quantities of ceiling grids.
Aluminum: Aluminum is a more expensive material, which means that aluminum ceiling grids tend to be priced higher than steel grids. However, the increased cost can be justified by its lightweight nature, superior corrosion resistance, and aesthetic advantages, especially for projects that require a higher-end finish.
When selecting between steel and aluminum, it is essential to weigh the budgetary constraints against the specific performance and aesthetic requirements of the project.
4. Environmental Impact: Steel vs. Aluminum
Sustainability is becoming an increasingly important factor in construction, and both steel and aluminum offer unique advantages when it comes to environmental impact.
Steel: Steel is 90% recyclable, and the recycling process uses less energy compared to the production of new steel. Many steel ceiling grids are made from recycled steel, contributing to a circular economy and reducing the overall environmental footprint of the material.
Aluminum: Aluminum is also highly recyclable, and recycling aluminum saves up to 90% of the energy required to produce new aluminum from raw materials. Additionally, aluminum is lightweight, which means lower transportation emissions compared to heavier materials like steel. However, the initial production of aluminum can have a higher environmental impact than steel due to the energy-intensive extraction process.
Both materials can be considered eco-friendly when recycled, but aluminum’s lower transportation costs and high recyclability make it a more sustainable option in certain scenarios.
5. Applications of Steel and Aluminum Ceiling Grids
Choosing between steel and aluminum ceiling grids often depends on the specific needs of the space and the intended application.
Steel Ceiling Grids: Steel is well-suited for commercial and industrial applications where strength, durability, and affordability are paramount. It is often used in large office buildings, schools, hospitals, and factories where heavy loads need to be supported.
Aluminum Ceiling Grids: Aluminum is ideal for residential spaces, high-end commercial environments, or areas where aesthetics and lightweight materials are important. It is commonly found in modern office spaces, museums, galleries, and luxury hotels.
Both materials can be used for a variety of ceiling grid systems, but understanding the specific demands of the project will guide the decision-making process.
6. Installation and Maintenance: Steel vs. Aluminum Ceiling Grids
The installation process and long-term maintenance requirements can also influence the choice of material.
Steel Ceiling Grids: Steel grids are heavier and require more effort during installation. They may require specialized tools and equipment for handling and installation. Over time, steel may require maintenance to ensure the protective coating remains intact to prevent rust and corrosion.
Aluminum Ceiling Grids: Aluminum grids are easier to handle and install due to their lightweight nature. They typically require less maintenance because of their natural corrosion resistance, making them a low-maintenance option for areas with high humidity or moisture.
Conclusion: Steel vs. Aluminum Ceiling Grids
Ultimately, the choice between steel and aluminum for your ceiling grid system will depend on the specific requirements of your project, including budget, load-bearing capacity, aesthetic preferences, and environmental considerations. Steel is the more cost-effective and durable option, while aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance and aesthetic flexibility.
By understanding the key differences between these two materials, you can select the right ceiling grid system to meet your needs and ensure a high-performance, visually appealing ceiling solution for your space.
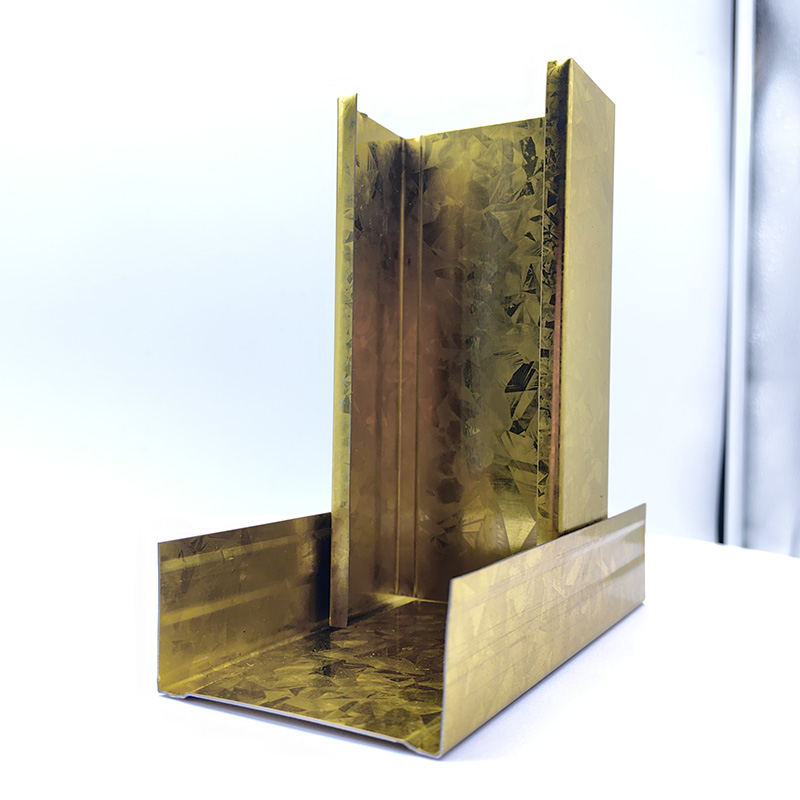
A Double Anti-Rust Gold Partition Wall Stud is a type of steel stud commonly used in the co...
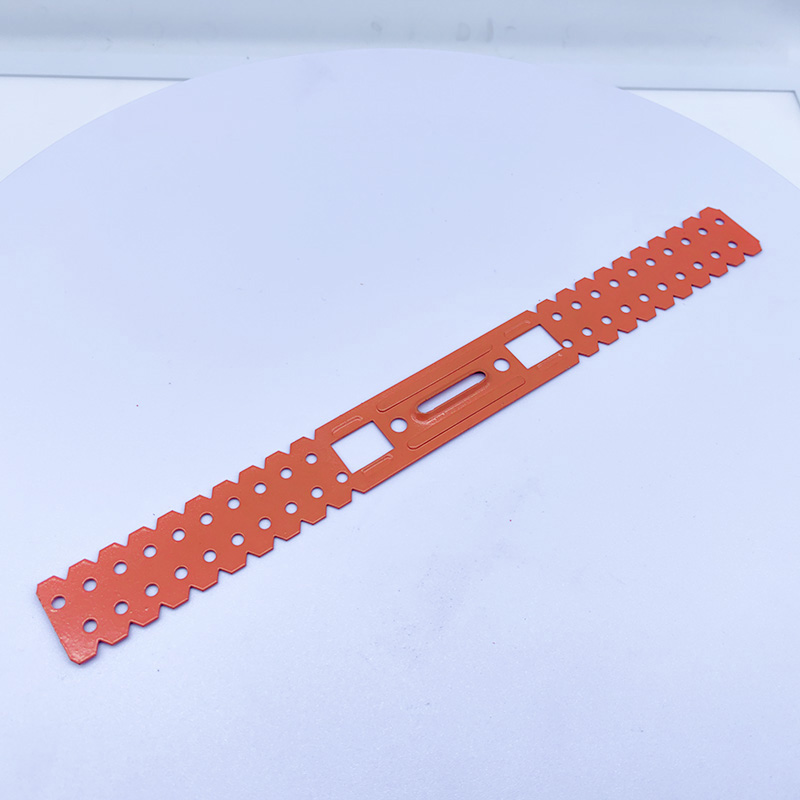
A CD UD Profile Furring Clip U Clamp is a type of metal fastening component used in the ins...
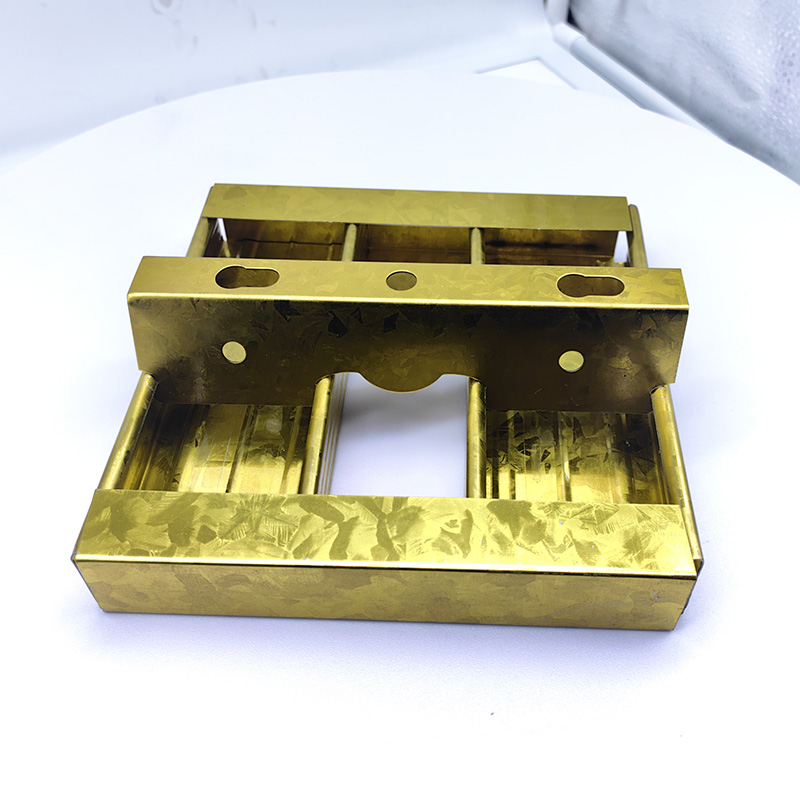

A 60mm Ceiling Grid refers to a type of suspended ceiling system, commonly used in commerci...
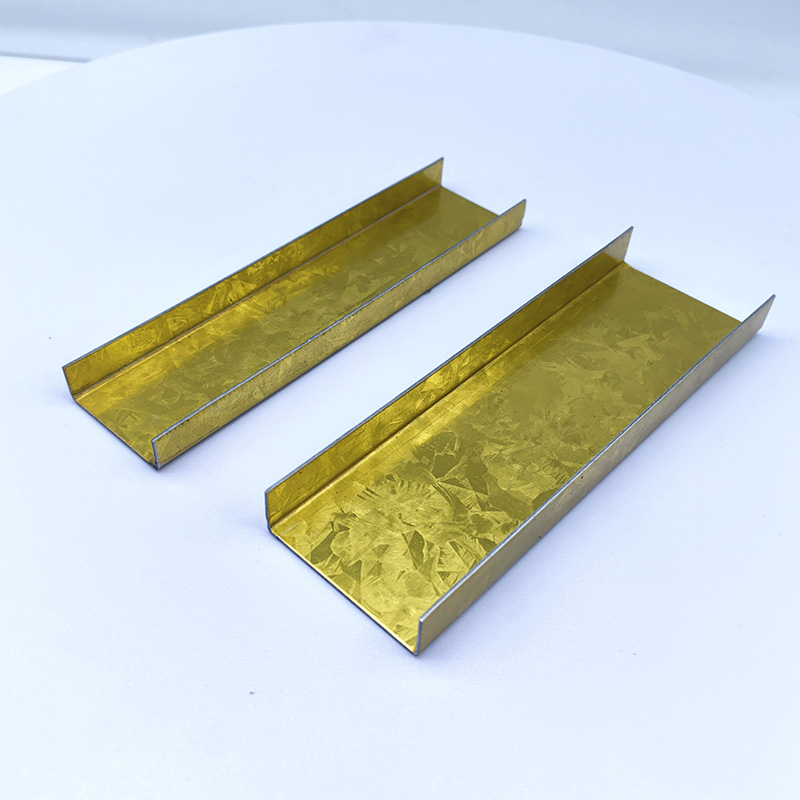
38mm Main Tee and 50mm Main Tee refer to the widths of the main tee profiles used in suspen...

