Ceiling Grid Material Selection: Which One Suits Your Needs Best?
2025-02-11 14:03:37
Ceiling grids are an essential component of suspended ceiling systems. They not only affect the overall aesthetic but also play a significant role in safety and longevity. With so many material options available on the market, how do you choose the one that best fits your needs? This article will provide a detailed analysis of the pros and cons of several common materials, helping you make an informed decision.
1. Aluminum Alloy Grid: Lightweight and Durable Mainstream Choice
Advantages:
· Lightweight: Aluminum alloys have a low density, making them easy to handle and install, reducing the load on building structures.
· High Strength: Aluminum alloy grids, after special treatment, offer high strength and rigidity, able to bear significant weight.
· Corrosion Resistance: The surface of aluminum alloys forms a dense oxide film, effectively resisting corrosion and extending the lifespan.
· Excellent Fire Resistance: Aluminum is a non-combustible material, which helps prevent the spread of fire and ensures personal safety.
· Variety of Surface Treatments: It can be customized with different finishes such as spraying, anodizing, and wood grain printing to match various decorative styles.
Disadvantages:
· Relatively higher cost compared to other materials.
Suitable Environments: Offices, malls, hospitals, schools, and other places where fire resistance and durability are critical.
2. Steel Grid: Economical and Cost-Effective Choice
Advantages:
· Low Cost: Steel is relatively inexpensive, making it a cost-effective option for projects with a tight budget.
· High Strength: Steel has high strength and rigidity, capable of bearing heavy loads.
· Strong Load-Bearing Capacity: Steel grids are often used in environments where heavy equipment needs to be supported, such as server rooms and warehouses.
Disadvantages:
· Heavy Weight: Steel is denser, making it more difficult to handle and install.
· Rusting: Steel can rust in humid environments, affecting both its appearance and lifespan.
· Moderate Fire Resistance: Steel loses strength at high temperatures, which could pose a safety risk.
Suitable Environments: Locations with budget constraints and less stringent fire requirements, such as warehouses and underground parking lots.
3. PVC Grid: Special Choice for Water and Moisture Resistance
Advantages:
· Lightweight: PVC has a low density, making it easy to transport and install.
· Water and Moisture Resistant: PVC performs well in humid environments, making it ideal for bathrooms, kitchens, and swimming pools.
· Corrosion Resistant: PVC resists acid and alkali corrosion, ensuring a long lifespan.
· Easy to Clean: PVC has a smooth surface that is easy to maintain and clean.
· Moderate Price: PVC is generally affordable and offers good value for money.
Disadvantages:
· Lower Strength: PVC has lower strength and rigidity compared to metal options, limiting its load-bearing capacity.
· Poor Heat Resistance: PVC can deform under high temperatures, posing a safety concern.
· Prone to Aging: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can cause PVC to degrade and affect its durability.
Suitable Environments: Bathrooms, kitchens, swimming pools, and other humid environments.
4. Wooden Grid: Natural and Warm Personalized Choice
Advantages:
· Natural Texture: Wooden materials have a natural texture and color, creating a warm and inviting atmosphere.
· Warm Feel: Wood provides a comfortable tactile experience, enhancing the overall comfort of a space.
· Personalized Decoration: Wood can be carved, stained, or treated to create unique decorative effects.
Disadvantages:
· Susceptible to Moisture and Deformation: Wood can easily absorb moisture and warp, impacting both aesthetics and longevity.
· Poor Fire Resistance: Wood is flammable, which poses potential safety risks.
· Requires Regular Maintenance: Wood needs regular treatments to prevent rot, insects, and other forms of deterioration, leading to higher maintenance costs.
Suitable Environments: Cafes, restaurants, homes, and other places seeking a natural or rustic style.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Ceiling Grid Materials:
· Budget: Different materials come with varying price tags, so it's essential to choose one that fits within your budget.
· Environment: Consider factors like humidity, temperature, and fire safety requirements in the environment where the ceiling grid will be used.
· Decorative Style: Select a material and color that complements the overall interior design and ambiance of the space.
· Load-Bearing Needs: Choose the appropriate material based on the weight-bearing requirements of the ceiling grid.
Conclusion:
There is no one-size-fits-all material for ceiling grids. The ideal material depends on your specific needs and circumstances. We hope this article has provided valuable insights to help you make a well-informed decision and create a visually appealing, functional, and durable ceiling system.
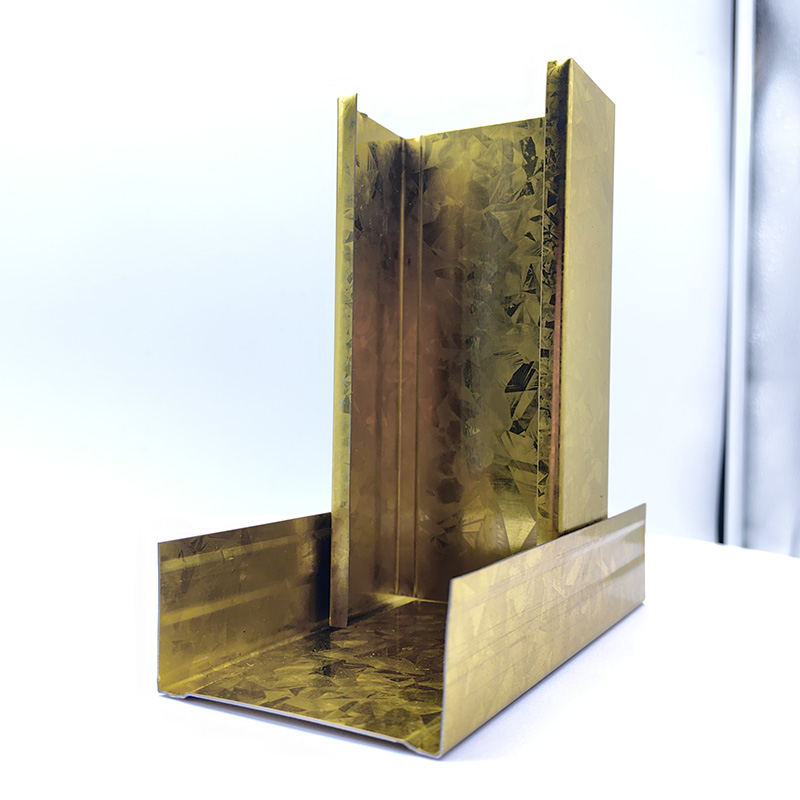
A Double Anti-Rust Gold Partition Wall Stud is a type of steel stud commonly used in the co...
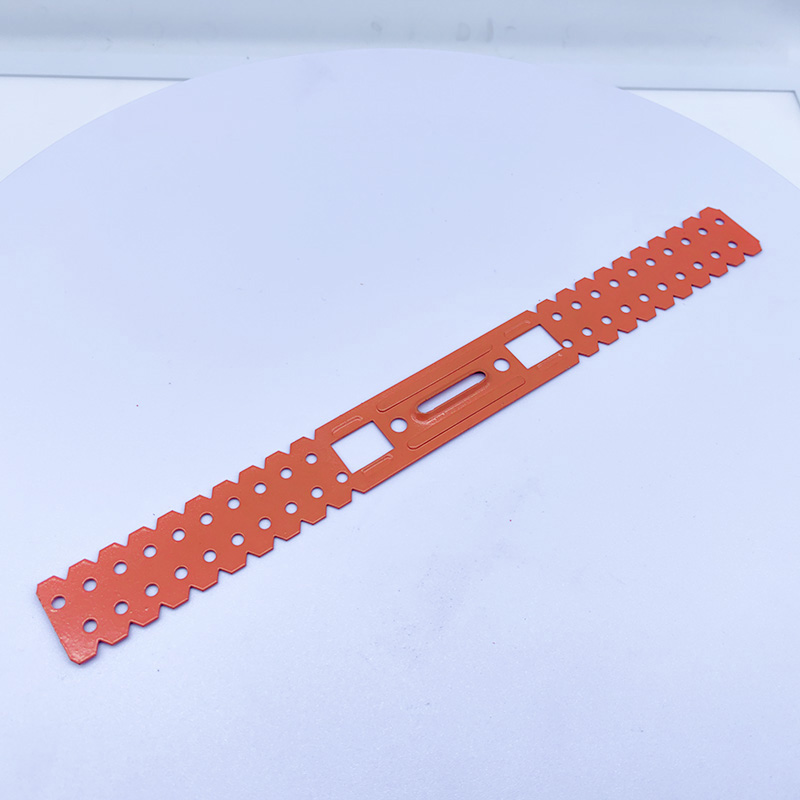
A CD UD Profile Furring Clip U Clamp is a type of metal fastening component used in the ins...
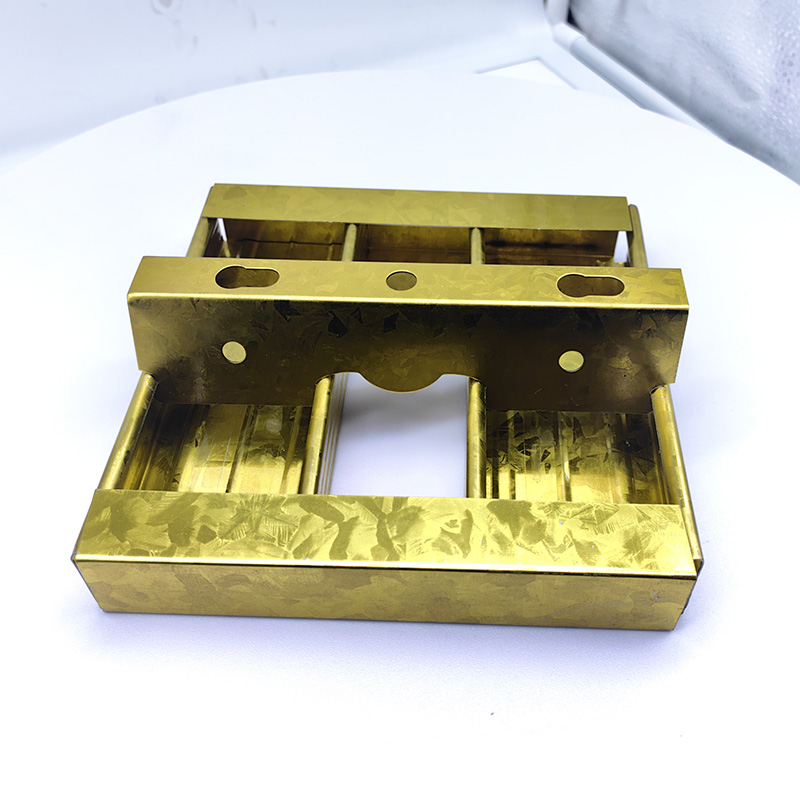

A 60mm Ceiling Grid refers to a type of suspended ceiling system, commonly used in commerci...
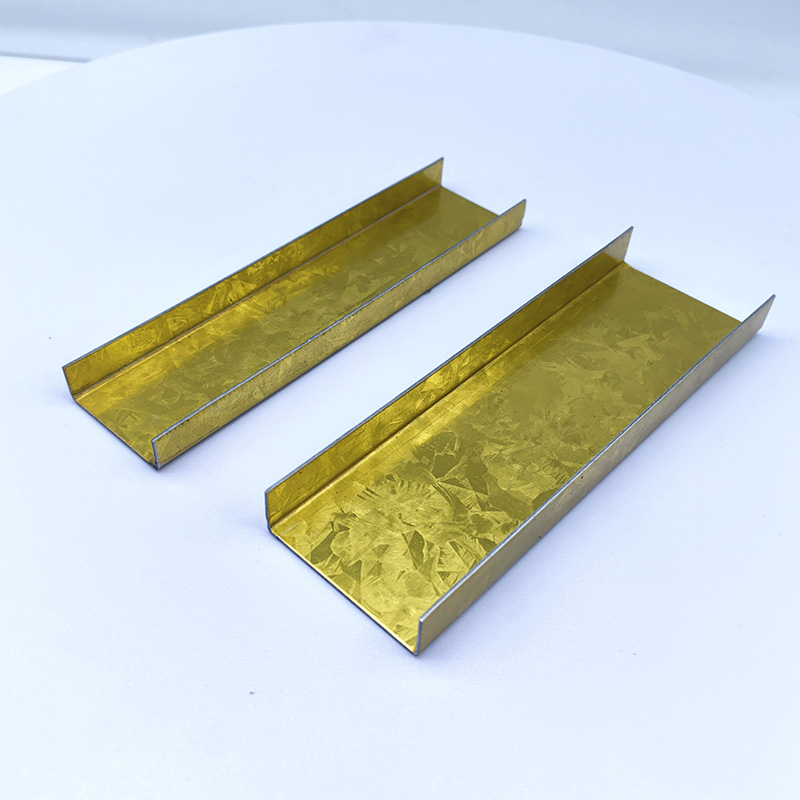
38mm Main Tee and 50mm Main Tee refer to the widths of the main tee profiles used in suspen...

