The Environmental Impact of Drywall Partitions: Sustainability Considerations
2024-11-09 13:56:20
The environmental impact of drywall partitions is increasingly relevant as construction sectors emphasize sustainability. Here are key sustainability considerations around drywall partitions:
1. Material Sourcing and Composition
Gypsum Mining: Drywall, primarily made from gypsum, relies heavily on mining, which disrupts natural habitats and leads to land degradation. Some drywall includes recycled gypsum, which helps reduce reliance on virgin materials.
Synthetic Gypsum: An alternative to mined gypsum, synthetic gypsum is a byproduct of coal power plants. This recycling reduces landfill waste, but its use is also tied to fossil fuel emissions from coal plants.
2. Energy Use in Production
Manufacturing Emissions: The production of drywall involves high-energy processes, including heating gypsum to remove moisture and forming it into sheets. These processes contribute to CO₂ emissions. Innovations in energy-efficient production methods or renewable energy use can mitigate these impacts.
Transportation Footprint: Drywall is heavy and costly to transport, contributing to a significant carbon footprint, especially when materials are imported. Locally sourced materials reduce this impact.
3. Waste and End-of-Life Considerations
High Waste Rates: Drywall installation generates waste due to cuts and offcuts, and unused pieces often end up in landfills.
Limited Recycling Options: While recycling drywall is possible, it remains limited due to contamination concerns and challenges in separating gypsum from other materials. Increasing recycling rates or developing more recyclable alternatives would significantly reduce environmental impact.
4. Indoor Air Quality and Health
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Many types of drywall are coated or treated with compounds that emit VOCs, which can affect indoor air quality. Low-VOC or zero-VOC options are better for health and environmental quality.
Moisture and Mold: Drywall is susceptible to moisture, leading to mold growth. Mold-resistant drywall products are available, though they may contain additional chemicals, impacting sustainability and indoor health.
5. Sustainable Alternatives and Innovations
Eco-Friendly Drywall: Some manufacturers are producing drywall using recycled paper and eco-binders, making the products biodegradable or easier to recycle.
Alternative Materials: Materials like hempcrete, cork, and recycled wood panels offer sustainable partition options that reduce reliance on gypsum and may have a lower environmental impact.
6. Lifecycle Analysis and Circularity
Cradle-to-Grave vs. Cradle-to-Cradle: For a more sustainable approach, drywall should ideally follow a cradle-to-cradle lifecycle, where materials are recycled or reused. Currently, most drywall follows a cradle-to-grave lifecycle, ending up as waste post-demolition.
Conclusion
While drywall partitions are widely used due to cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, their environmental footprint is significant. Sustainable approaches in sourcing, production, recycling, and alternative materials can mitigate these impacts, offering eco-friendly options for construction professionals and environmentally conscious developers.
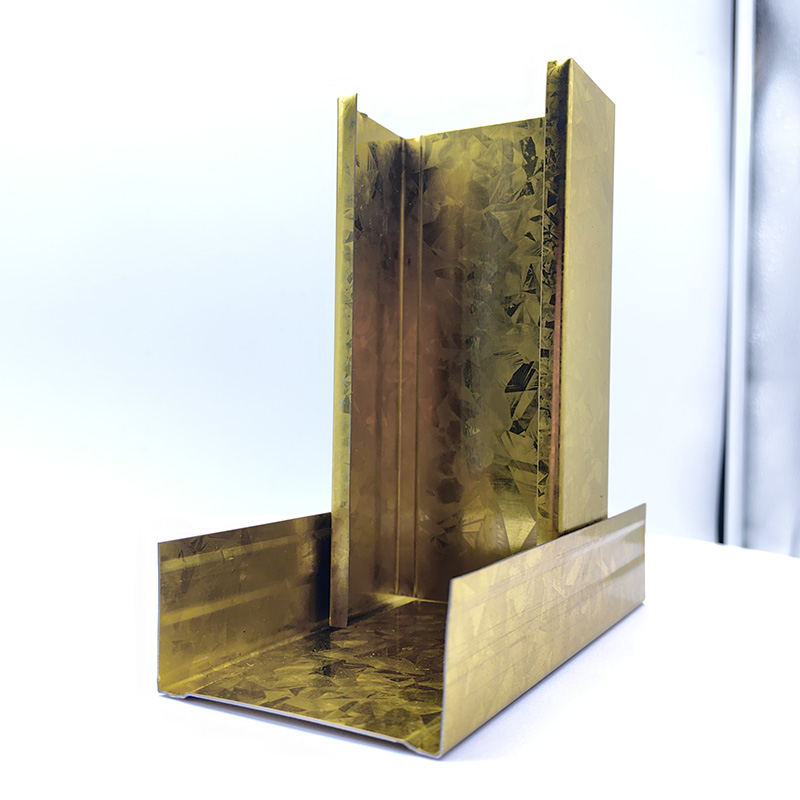
A Double Anti-Rust Gold Partition Wall Stud is a type of steel stud commonly used in the co...
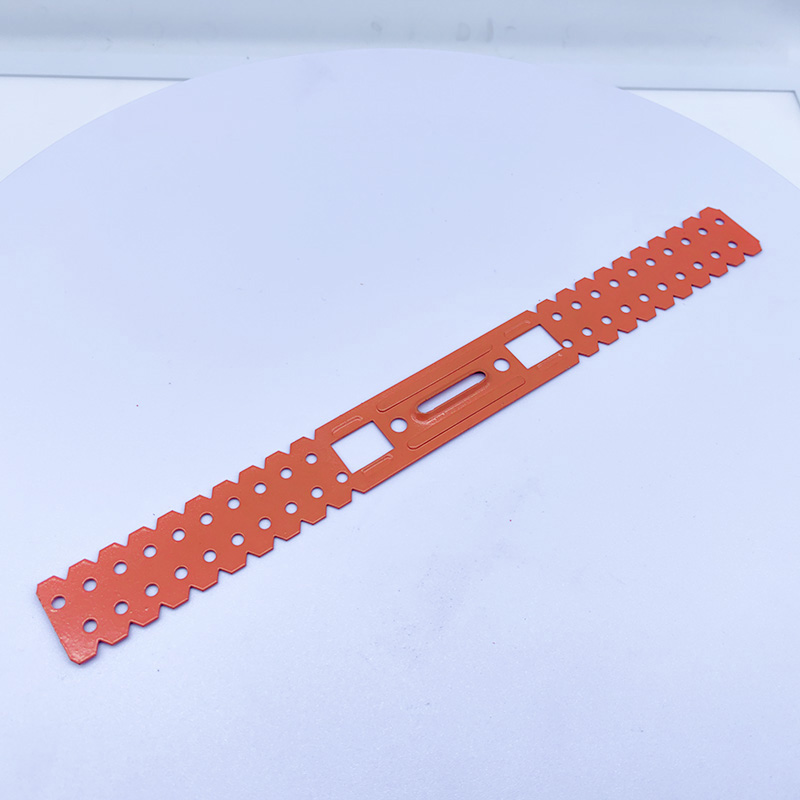
A CD UD Profile Furring Clip U Clamp is a type of metal fastening component used in the ins...
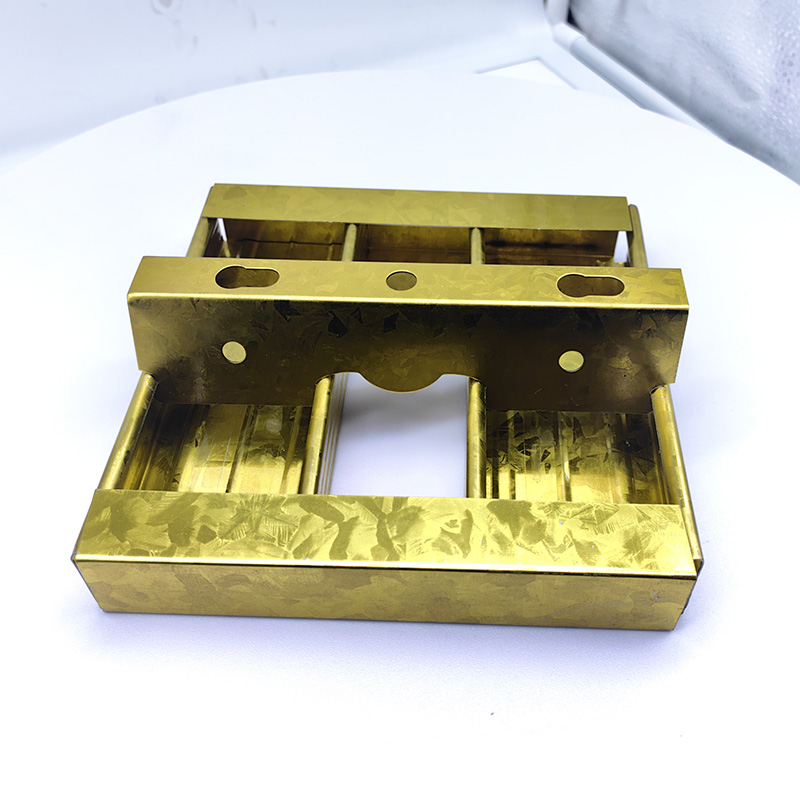

A 60mm Ceiling Grid refers to a type of suspended ceiling system, commonly used in commerci...
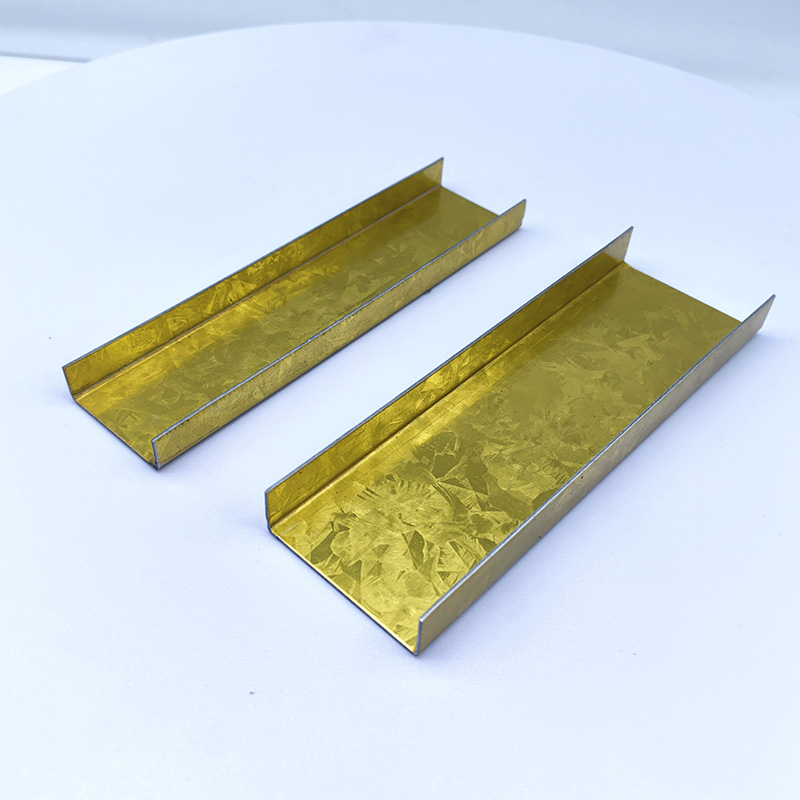
38mm Main Tee and 50mm Main Tee refer to the widths of the main tee profiles used in suspen...

